The Role of MRI in Diagnosing Neurological Disorders
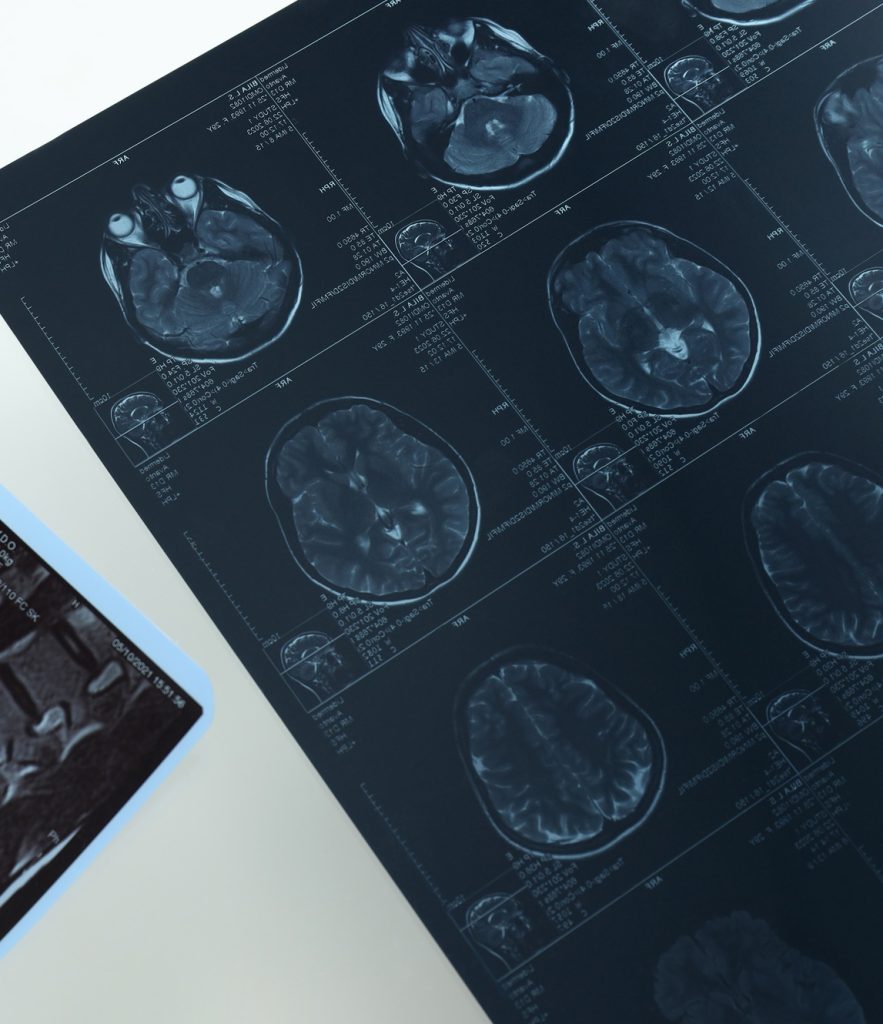
MRI is a key tool in diagnosing neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis, strokes, and brain tumors. It provides detailed brain images, helping doctors detect abnormalities without invasive procedures.
MRI Contrast: Why It’s Used and What to Expect
MRI contrast agents enhance image clarity, helping doctors detect tumors, infections, and vascular conditions. Patients should know how contrast works, its safety profile, and potential side effects.
Tips for a More Comfortable Experience During an MRI

Many patients experience anxiety before an MRI scan. Strategies like deep breathing, distraction techniques, and open MRI options can help reduce stress and improve the overall experience.
Claustrophobia in MRI: What You Should Know
MRI scans can feel like a tight squeeze, sparking claustrophobia. Knowing what triggers it and how to cope makes this vital test less daunting—here’s the rundown.
Why MRI Scans Take So Long: A Patient’s Guide
MRI scans can take 15 minutes to over an hour, depending on the type of scan. Understanding the reasons behind the duration can help patients prepare and remain comfortable during the procedure.
Open vs. Closed MRI: Which One is Right for You?
Open and closed MRIs differ in design and patient experience. While closed MRIs provide higher-quality images, open MRIs offer comfort for claustrophobic or larger patients. Choosing the right option depends on individual needs.
MRI vs. CT Scan: Which One Do You Need?
MRI and CT scans serve different purposes in medical imaging. Understanding their differences, risks, and benefits can help patients make informed decisions about which scan is best suited for their condition.
Understanding MRI: What to Expect and How to Prepare
MRI scans provide detailed images of the body’s internal structures. Patients should prepare by following safety guidelines, wearing appropriate clothing, and understanding the non-invasive nature of the procedure.
